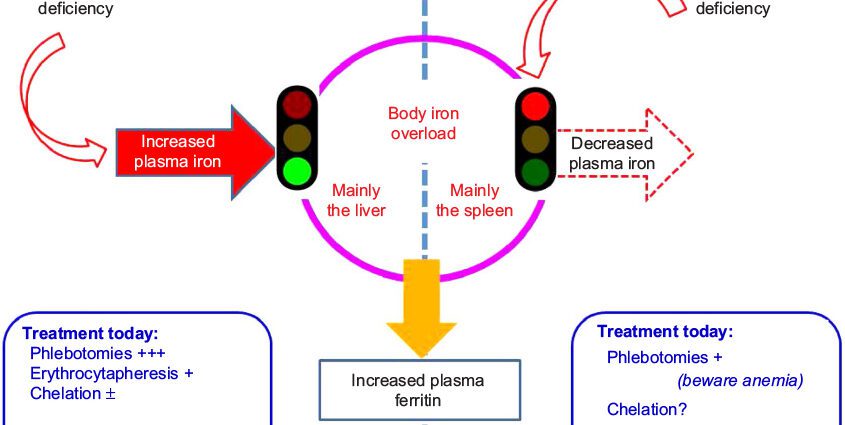
Treatment, management, prevention of hemochromatosis
Treatment of hemochromatosis is based on בלאַדלעטטינג (also called phlebotomies). They aim to lower the iron level in the blood and reduce iron deposits in the body without causing iron deficiency anemia.
The procedure is identical to that practiced during a blood donation. It is recommended to drink water after bleeding.
It is a simple, inexpensive and effective treatment, usually carried out between 4 and 6 times a year, without impact on the patient’s life, especially since the bleeding can be performed at home.
The doctor defines an amount of blood to be taken קעסיידער דערשייַנען in the patient taking into account his age, weight and height. Initially, weekly bloodletting is necessary and maintained as long as iron overload is observed. When the level of ferritin in the blood falls below 50 μg / L, they are carried out monthly or quarterly as the case may be to maintain a level of ferritin in the blood below 50 μg / L. They will be maintained for life.
This treatment does not cure the disease.
In pregnant women, bleeding is not practiced throughout the pregnancy. Iron supplementation is not necessary.
The other complications of the disease (cirrhosis, heart failure or diabetes) are the subject of specific treatment.
Note that no diet can replace treatment by bleeding. The patient is recommended to follow a normal diet and limit alcohol consumption.
בענעפיץ פון באַהאַנדלונג
With treatment, the fatigue often seen in patients with hemochromatosis is reduced. Especially, when the treatment is started early, it helps to avoid serious complications of the disease (damage to the heart, liver and pancreas) and thus lengthen the life expectancy of patients.
No change in the habits of patients is to be considered in hemochromatosis apart from the rules of hygiene of life which include a normal diet and a reduction in alcoholic beverages if excesses were previously practiced.
Patients are monitored in the hepato-gastroenterology departments. In people at risk, a genetic consultation is completely indicated in order to detect the disease early and take the necessary therapeutic measures.
In France, advanced forms of hemochromatosis are one of the 30 long-term conditions (ALD 30).