ינהאַלט
Systemic scleroderma: definition, treatment
Scleroderma are inflammatory diseases causing sclerotic thickening of the skin. There are two main forms: localized scleroderma, also called “morphea”, which concerns the skin and sometimes in the deep forms the underlying musculo-aponeurotic and skeletal planes and systemic scleroderma which concern the skin and organs.
Definition of systemic scleroderma
Systemic scleroderma is a rare disease affecting 3 women for every man, most commonly occurring between the ages of 50 and 60, which causes tissue fibrosis of the skin and certain organs, in particular the digestive tract, lungs, kidneys and heart. The involvement of these last 3 organs often causes serious complications.
Its development is usually spread over years, marked by flare-ups.
Raynaud סינדראָום
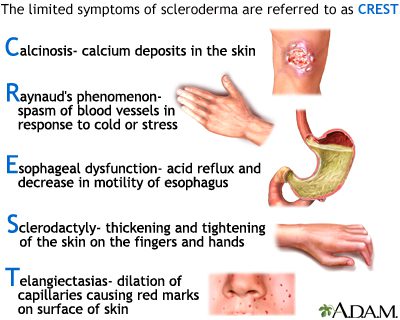
Raynaud’s syndrome is characterized by the bleaching of certain fingers in the cold. It is almost always the first sign of scleroderma, especially when it is bilateral, appearing before the other signs from a few weeks to a few years (the shorter the delay, the more unfavorable the prognosis) and it exists in 95% of cases scleroderma.
The doctor performs a nail capillaroscopy (examination with a powerful magnifying glass of the vessels of the cuticle and the nail fold) showing in favor of scleroderma:
- a rarefaction of the capillary loops,
- mega-capillaries
- sometimes the existence of pericapillary edema
- cuticular hyperkeratosis,
- עריטהעמאַ,
- microhemorrhages visible to the naked eye.
Skin sclerosis
To the fingers
The fingers are initially swollen and coiled with a tendency for the fingerprints to disappear. Then the skin becomes tight, indurated giving a “sucked” aspect of the finger pulps
Then the fingers gradually taper and retract in flexion.
Complication of sclerosis, painful ulcerated sores occur on the pulpitis
אנדערע געביטן
Sclerosis may spread to the face (the face smooths and freezes; there is a tapering of the
nose and reduced opening of the mouth which is surrounded by radiate folds in “purse pocket”), limbs and trunk giving a smooth and sheathed appearance to the shoulders, trunk and limbs.
טעלאַנגיעקטאַזיאַ
These are small purplish vessels that group together in purplish spots of one to 2 millimeters, and which develop on the face and on the extremities.
calcinoses
These are hard nodules, white when they are superficial, which can, when they come into contact with the skin, leave a chalky mush. They are more common on the hands and legs.
Mucosal involvement
The oral mucosa is often dry as well as the eyes. This is called sicca syndrome.
Organ sclerosis
The digestive tract
Involvement of the esophagus is present in 75% of cases, manifested by gastroesophageal reflux, difficulty swallowing, or even esophageal ulcerations.
The small intestine is also affected by fibrosis or even villous atrophy, sometimes responsible for a malabsorption syndrome, accentuated by a slowing down of intestinal peristalsis, causing microbial overgrowth and exposing the risk of intestinal pseudo-obstruction.
The lungs and the heart
Pulmonary interstitial fibrosis occurs in 25% of patients, responsible for respiratory disorders that can lead to chronic respiratory failure, a major cause of death in affected patients.
The second leading cause of death is pulmonary arterial hypertension, due to pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary artery damage or cardiac damage. The latter is linked to myocardial ischemias, “myocardial Raynaud’s phenomenon” and fibrosis.
קידניז
Kidney damage results in malignant hypertension and kidney failure
Locomotor device
There is damage to the joints (polyarthritis), tendons, bones (demineralization, destruction of distal bones) and muscles (muscle pain and weakness).
Treatment of systemic scleroderma
Fight against fibrosis
Monitoring is essential and there are many treatments that can be tried because their effectiveness varies greatly from person to person. Among the treatments used, we can mention colchicine, D-penicillamine, interferon γ, cortisone, ciclosporin, etc.
Regular physical exercise, massages and rehabilitation attempt to maintain mobility and combat muscle atrophy.
Raynaud סינדראָום
In addition to protection against the cold and stopping smoking, vasodilators such as calcium channel blockers: dihydropyridines (nifedipine, amlodipine, etc.) or benzothiazines (diltiazem) are used. If the calcium channel blockers are ineffective, the doctor prescribes other vasodilators: prazosin, converting enzyme inhibitors, sartans, trinitrin, iloprost, etc.
טעלאַנגיעקטאַזיאַ
They can be attenuated by a pulsed dye vascular laser or KTP.
Subcutaneous calcinosis
The doctor prescribes bandages, even colchicine. Surgical excision of calcinosis is sometimes necessary.
Treatment of manifestations of other organs
דיגעסטיווע שעטעך
It is necessary to respect the hygieno-dietary measures of gastroesophageal reflux: elimination of acidic foods and alcohol, eating meals in a seated position, use of several pillows to sleep. The doctor prescribes proton pump inhibitors to limit stomach acidity.
In the event of malabsorption, linked to a microbial proliferation favored by the slowing of intestinal peristalsis, the doctor prescribes antibiotics intermittently and cyclically one to two weeks every month (ampicillin, tetracyclines or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole), associated with supplementation of iron, folic acid and vitamin B12.
לונגען און הארץ
Against pulmonary interstitial fibrosis, cyclophosphamide is used alone or in combination with cortisone. Secondary pulmonary infections are treated with antibiotics and the risk of worsening pulmonary fibrosis is limited by vaccination against influenza and pneumococcus.
Against pulmonary arterial hypertension, vasodilators such as nifedipine are used. iloprost and esoprostenol.
For myocardial irrigation, calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors are used.
רעינס
ACE inhibitors such as captopril or vasodilators such as sartans limit arterial hypertension and associated renal failure.
Muscle and joint damage
The doctor prescribes non-steroidal or steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (cortisone) for joint pain