ינהאַלט
כייקאַפּס
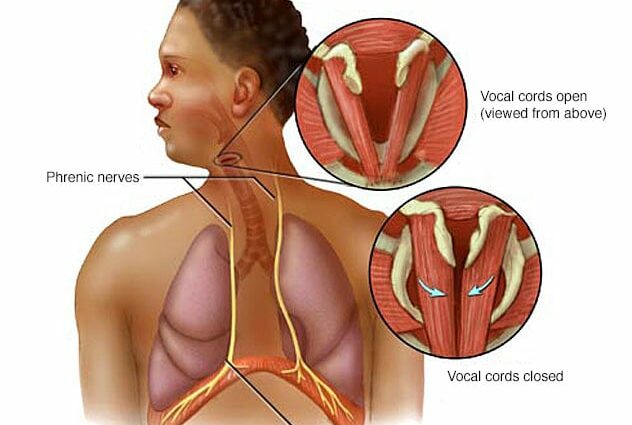
Hiccups are the common name (we speak of myoclonie phrénoglottique in medical terms) to denote a succession of involuntary and repeated spasmodic contractions of the diaphragm associated with closure of the glottis and often contraction of the intercostal muscles. Ce סלר occurs suddenly and uncontrollably. It results in a series of characteristic sonic “hics”.
Typology and causes of hiccups
The hiccups are probably due to stimulation of the phrenic nerves, vagus nerves or the brainstem located in the brain. These stimuli trigger the hiccup reflex.
There are two types of hiccups. The most common is the hiccups said benign (or acute), which usually lasts no more than a few minutes, or even just a few seconds, then ceases spontaneously. It is due to stimulation of the vagus or phrenic nerve, most often of intestinal origin. However, it can be linked to many different factors: ingestion of food too quickly or in too much quantity, aerophagia, pregnancy, excessive smoking, laughing, coughing, sudden changes in temperature, stress, alcohol abuse, consumption of drinks. sparkling …
Much more rarely, some people can develop chronic hiccups (or rebellious hiccups). It is said to be persistent when its duration exceeds 48 hours, and refractory when it lasts for more than a month. Hiccups are then considered a disease. The causes of this hiccup are very often pathological, that is to say linked to various diseases affecting in particular the phrenic nerve, the vagus nerve or the brainstem. It may also be due to central nervous system disorders, metabolic disorders, or drugs with this side effect. People over 50 are the age group most affected by this very rare form of hiccups.
Treatment of hiccups
As the name suggests, mild hiccups are completely harmless and don’t require special treatment since they usually go away on their own fairly quickly. On the other hand, there is a whole series of means or “remedies” which would be able to stop hiccups. Most are based on stimulating the glottis, increasing the level of carbon dioxide in the lungs, the rate of breathing and diversion. Among the sixty techniques identified, we can cite the following:
- Temporarily stop breathing (voluntary prolonged apnea),
- Suddenly interrupt breathing thanks to a surprise effect,
- Drink a large glass of water in one go,
- Drink a glass of water, covering your ears and tilting your head back,
- Pull the tongue forward,
- Rub the palate with your finger,
- Suck on an ice cube or swallow crushed ice,
- Swallow an acidic or sweet product (lemon, powdered sugar, dry bread, ginger, etc.),
- Place a cold object on the stomach at the level of the diaphragm,
- Cause a sneeze by breathing in pepper …
This non-exhaustive list of popular and sometimes absurd remedies should be taken with caution: the majority of these methods are transmitted by tradition without it being possible to determine with precision whether they are effective or not. For chronic hiccups, treatment is determined based on the disease that triggered it. Several methods including stimulation of the wall of the pharynx with a probe, and drugs (muscle relaxants, antidepressants, anticonvulsants) are however used to try to reduce the frequency of hiccups and provide relief to the person who suffers from them.
פאַרהיטונג פון כייקאַפּס
It is difficult to prevent the onset of hiccups, which occur quite randomly, but we can try to reduce the risks. avoiding eating too quickly, און ווי too much tobacco, alcohol, or soft drinks, די סטרעספאַל סיטואַטיאָנס אָדער די sudden changes in temperature.
Complementary approaches to hiccups
Many methods exist to fight against hiccups.
Classical remedies
In addition to those mentioned above, you can also try other tips.
- Lie on your back and bend your knees to keep them pressed against your chest.
- Take a piece of sugar soaked in vinegar.
- Let three lumps of sugar melt in your mouth.
- Squeeze your little finger tightly for about XNUMX seconds.
טהעראַפּיעס
For cases of chronic hiccups, it is possible to use complementary therapies such as osteopathy or acupuncture … provided that the origin of the hiccups is known and that the disease or problem in question has already been treated medically. . Indeed, chronic hiccups can be due to serious illnesses and it is essential to start by looking for the cause. Going directly to complementary therapy without going through a medical check-up could represent a loss of chance to be treated for a progressive disease in time.
כאָומיאָופּאַטי
Since hiccups resemble a diaphragm cramp, homeopathy offers solutions traditionally used for muscle cramps such as Cuprum metallicum, Compound Aesculus, Tabacum and Cicuta viros.