ינהאַלט
בלידינג פון די נאָז: אַלע איר דאַרפֿן צו וויסן וועגן אַ בלידינג נאָז
Bleeding from the nose, or epistaxis, is a common and often mild occurrence. However, in some cases, having a bleeding nose can be a sign of a more serious health problem. An emergency consultation is particularly recommended in case of persistent or repetitive nosebleeds.
Description of a nosebleed
Bleeding nose: what is epistaxis?
Epistaxis is the medical term for a nosebleed. It is characterized by a flow of blood from the nasal cavities.
אין וואָס קאַסעס זאָל איר זיין זארגן?
In the majority of cases, having a bleeding nose is a benign and temporary phenomenon. However, in some cases, epistaxis can be a sign of a more serious health problem. Some signs can alert, such as persistent or repeated nosebleeds.
Causes of a nosebleed
Essential epistaxis, the most common case of nosebleeds
In 60% of cases, the epistaxis is said to be essential. Benign and transient, the nosebleed is due to the rupture of blood capillaries at the level of the vascular spot, point of convergence of the arterial systems of the nasal fossa.
Essential epistaxis is often caused by vascular fragility which can be caused or accentuated by:
- זון ויסשטעלן ;
- a physical effort ;
- untimely scratching.
These causes are particularly common in children with nosebleeds. They are also found in adolescents and young adults. A nosebleed can also occur in older people.
Bleeding nose: what are the other possible causes?
While essential epistaxis is the most common form of nosebleed, there are others with various causes. In this case, the bleeding is usually the result of an underlying abnormality or disease. The epistaxis can then have a localized or generalized cause.
A nosebleed can have a localized origin when it is due to:
- צו טראַוומע ;
- אָנצינדונג, such as rhinitis or sinusitis, which can be caused by an ENT infection;
- די אָנוווקס, benign or malignant, which can be localized in different places of the nasal cavities.
A nosebleed can also have a generalized origin when it is the consequence of an underlying disorder such as:
- דיכייפּערטענשאַן ;
- a hemorrhagic disease caused by thrombocytopenia or thrombopathy, taking certain medications, haemophilia, or even certain forms of purpura;
- a וואַסקיאַלער קרענק such as Rendu-Osler disease or ruptured intracavernous carotid aneurysm.
The consequences of a nosebleed
A nosebleed can manifest itself in different ways. He can be :
- more or less abundant, ranging from simple drip to prolonged flow;
- יונאַלאַטעראַל אָדער ביילאַטעראַל, occurring at a single nostril or both nostrils simultaneously;
- occasional or frequent ;
- transient or persistent.
Although a nosebleed is usually mild, there are certain signs that should alert you to limit the risk of a complication. Medical advice is particularly recommended if the nose bleeds profusely, persistently or frequently. The same is true if the nosebleed is accompanied by other symptoms such as pallor, weakness or tachycardia.
Treatment of a nosebleed
Bleeding nose: what to do if you have a nosebleed?
In the event of a nosebleed, it is advisable to:
- זיצן, whenever possible, in a quiet environment;
- do not tilt your head back to prevent blood from flowing to the throat;
- blow your nose to get rid of the blood clot (s) may have formed in the nasal cavities;
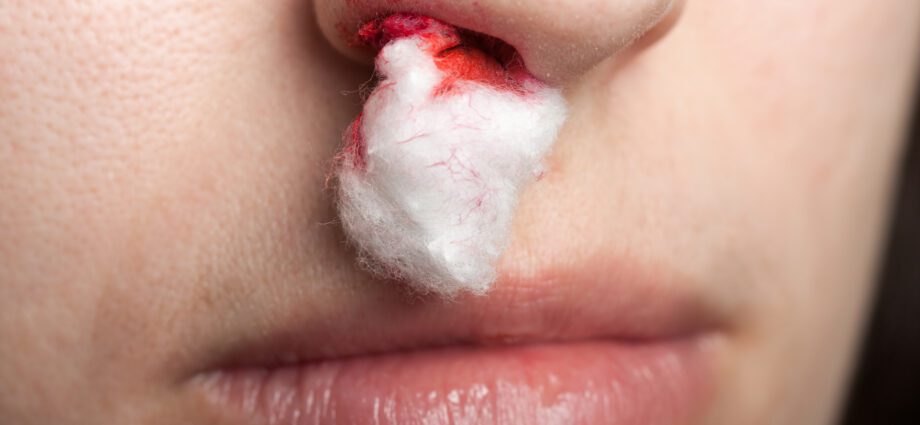
- limit the flow of blood through the nose using a handkerchief or cotton, for example;
- compress the wing of the nose for at least 10 minutes to stop the bleeding.
In addition to these measures, certain products, such as hemostatic pads, can also be used to help stop the bleeding.
Bleeding nose: when to consult?
If, despite all measures to stop the bleeding, the discharge persists, medical advice is necessary. An emergency consultation is also recommended if the bleeding is very profuse, repeats or is accompanied by other symptoms.
After the bleeding has stopped, several medical examinations may be done to understand the origin of the epistaxis. In first intention, a יגזאַם ORL is performed to identify a localized cause. Depending on the results obtained, a general medical examination may be necessary.
שרייבן: Quentin Nicard, science journalist סעפטעמבער קסנומקס |
וואָס איז די באַהאַנדלונג פון גלאָמערולאָנעפריטיס?
באַהאַנדלונג פון גלאָמערולאָנעפריטיס דעפּענדס אויף זייַן אָנהייב און קורס.
ווי אַ ערשטער-שורה באַהאַנדלונג, מעדיצין באַהאַנדלונג איז יוזשאַוואַלי שטעלן אין פּלאַץ צו רעדוצירן סימפּטאָמס און באַגרענעצן די ריזיקירן פון קאַמפּלאַקיישאַנז. א געזונט זאָרגן פאַכמאַן יוזשאַוואַלי פּריסקרייבז:
- אַנטיהיפּערטענסיוועס צו קאָנטראָלירן בלוט דרוק און באַגרענעצן הויך בלוט דרוק, אַ פּראָסט סימפּטאָם פון גלאָמערולאָנעפריטיס;
- דייורעטיקס צו פאַרגרעסערן די פּישעכץ רעזולטאַט און אָפטקייַט פון ורינאַטיאָן.
דערנאָך, אנדערע דרוגס קענען זיין פּריסקרייבד צו מייַכל די סיבה פון גלאָמערולאָנעפריטיס. דעפּענדינג אויף די דיאַגנאָסיס, דער דאָקטער קען, למשל, פאָרשרייַבן:
- אַנטיביאַטיקס, ספּעציעל אין קאַסעס פון פּאָסטן-סטרעפּטאָקאָקקאַל גלאָמערולאָנעפריטיס, צו האַלטן אַ ינפעקציע אין די קידניז;
- קאָרטיקאָסטעראָידס און ימיונאָסופּפּרעססאַנץ, ספּעציעל אין קאַסעס פון לופּוס גלאָמערולאָנעפריטיס, צו רעדוצירן די ימיון ענטפער.
אין אַדישאַן צו מעדיצין באַהאַנדלונג, אַ ספּעציפיש דיעטע קענען זיין ימפּלאַמענאַד אין פאַל פון גלאָמערולאָנעפריטיס. די דיעטע איז בכלל דיפּליטיד אין פּראָטעין און סאָדיום, און איז באגלייט דורך קאָנטראָל פון די סומע פון וואַסער ינדזשעסטאַד.
אויב די ריזיקירן פון ניר דורכפאַל איז הויך, דיאַליסיס קען זיין געוויינט צו ענשור די פילטריישאַן פון די קידניז. אין די מערסט שטרענג פארמען, אַ ניר טראַנספּלאַנט קען זיין קאַנסידערד.